Installation
- Tutoriales en YouTube
- Descarga los binarios compilados
- Compilar desde el código fuente
- Ejecutar usando Docker
- Ejecutar en Android
- Ejecutar MCC 24/7 en un Servidor Privado Virtual
Tutoriales en YouTube
Si no eres el tipo de persona que le gusten los tutoriales en texto, nuestra comunidad ha hecho videotutoriales disponibles en YouTube.
Descarga los binarios compilados
Puede descargar la última versión en nuestra sección de Versiones en Git Hub: Click Aquí
Compilar desde el código fuente
We recommend you to download our precompiled binary file from GitHub.
However, if you want to build the program from source code, please follow the guide.
Windows
Requisitos:
- Git
- .NET 7.0 or new-er or Visual Studio configured for C# app development
Tip
**If you want to modify the code, and you are new to C# or in programming in general, you might want to watch some C# tutorials, we recommend the ones listed in [Creating Bots](creating-bots.md#requirements) section.**
Clonar usando Git
Instala aquí: Git
- Cree una nueva carpeta donde quiera conservar el código fuente
- Entra en la carpeta que has creado, mantén
SHIFTy hazClick-derechoen el espacio vacío - Haga clic en
Git Bash Hereen el menú contextual - Clone el Repositorio de Git Hub escribiendo y ejecutando el siguiente comando:
git clone https://github.com/MCCTeam/Minecraft-Console-Client.git --recursive
- Una vez que el repositorio haya terminado de clonarse, puede cerrar la Consola de Comandos
- Abra la nueva carpeta clonada
Download translation resources (optional)
- Visit MCC project's homepage on Crowdin.
- You will need to log in to your Crowdin account in order to download.
- Click on the language you want to download the translation for.
- Find
MinecraftClient->Resources->Translations->MCC in-app text - Click the button
•••at the end of the line. - Click Download and save the file to folder
/MinecraftClient/Resources/Translations/. - Find
MinecraftClient->Resources->ConfigComments->Comments in the settings file - Click the button
•••at the end of the line. - Click Download and save the file to folder
/MinecraftClient/Resources/ConfigComments/. - Find
MinecraftClient->Resources->AsciiArt->ASCII Arts (Please use fixed-width fonts for editing) - Click the button
•••at the end of the line. - Click Download and save the file to folder
/MinecraftClient/Resources/AsciiArt/. - If you need to download a translation in another language, go to step 3 to continue.
Compilar usando Visual Studio
- Abra
MinecraftClient.slncon Visual Studio - Right click on
MinecraftClientsolution in theSolution Explorer - Haga clic en
Propiedades - Open up the
Buildtab and select configurationRelease - Presione
CTRL + Sy cierre el archivo - Right click on
MinecraftClientsolution in theSolution Explorer - Click
Build
If the build has succeeded, the compiled binary MinecraftClient.exe will be in MinecraftClient/bin/Release/net7.0/win-x64/publish folder.
Compilar manualmente usando .NET sin Visual Studio
- Abra la carpeta
Minecraft-Console-Clientque ha clonado o descargado - Abra PowerShell (
Click derechoen el espacio en blanco y haga clic enAbrir PowerShell, o en el Explorador de Windows:Archivo -> Abrir PowerShell) - Ejecute el siguiente comando para compilar el proyecto:
dotnet publish MinecraftClient -f net7.0 -r win-x64 --no-self-contained -c Release -p:UseAppHost=true -p:IncludeNativeLibrariesForSelfExtract=true -p:DebugType=None
If the build has succeeded, the compiled binary MinecraftClient.exe will be in MinecraftClient/bin/Release/net7.0/win-x64/publish folder.
Linux/macOS:
Tip
Si estás usando Linux, asumiremos que puedes instalar git por tu cuenta. Si no sabes cómo, búscalo para tu distribución, debería ser fácil. (Distros basadas en Debian: apt install git, Basado en Arch: pacman -S git)
Requisitos:
Git
Linux:
.NET SDK 7.0 or new-er
Clonar usando Git
- Abra una terminal y entre a la carpeta donde guardará MCC
- Clone el Repositorio de Git Hub escribiendo y ejecutando el siguiente comando:
git clone https://github.com/MCCTeam/Minecraft-Console-Client.git --recursive
Vaya a la carpeta que ha clonado (debería ser
Minecraft-Console-Client)If you want to download translation resources, please check out Download translation resources
Ejecute el siguiente comando para compilar el proyecto:
En Linux:
dotnet publish MinecraftClient -f net7.0 -r linux-x64 --no-self-contained -c Release -p:UseAppHost=true -p:IncludeNativeLibrariesForSelfExtract=true -p:DebugType=NoneTip
If you're using Linux that is either ARM, 32-bit, Rhel based, Using Musl, or Tirzen, find an appropriate RID for your platform and replace the
-r linux-64with an appropriate-r RID_NAME(Example for arm:-r linux-arm64)En macOS:
dotnet publish MinecraftClient -f net7.0 -r osx-x64 --no-self-contained -c Release -p:UseAppHost=true -p:IncludeNativeLibrariesForSelfExtract=true -p:DebugType=NoneTip
If you're not using MAC with Intel, find an appropriate RID for your ARM processor, find an appropriate RID and replace the
-r osx-64with an appropriate-r RID_NAME(Example for arm:-r osx.12-arm64)
Si la compilación ha tenido éxito, el binario compilado MinecraftClient estará en:
- Linux:
MinecraftClient/bin/Release/net7.0/linux-x64/publish/ - macOS:
MinecraftClient/bin/Release/net7.0/osx-x64/publish/
Usando Docker
Requisitos:
- Git
- Docker
Tip
Esta sección es para usuarios más avanzados, si no sabes cómo instalar git o docker, puede echar un vistazo a otras secciones para Git, y buscar sobre cómo instalar Docker en su sistema.
Warning
Preste atención a las advertencias, Docker funciona actualmente, pero debe iniciar los contenedores en el modo interactivo o MCC se bloqueará, estamos trabajando en resolver esto.
- Clone el Repositorio de Git Hub escribiendo y ejecutando el siguiente comando:
git clone https://github.com/MCCTeam/Minecraft-Console-Client.git --recursive
- Vaya a
Minecraft-Console-Client/Docker - Compile la imagen usando el siguiente comando:
docker build -t minecraft-console-client:latest .
Iniciar el contenedor usando Docker:
Danger
Hay un error con ConsoleInteractive que causa un fallo cuando un contenedor se inicia en modo sin cabeza(headless), así que necesita usar el modo interactivo. No reinicie los contenedores de manera clásica, Deténgalo y entonces inícielo con el modo interactivo (este comando), después de eso simplemente desacopla con CTRL + P y luego CTRL + Q.
# También puede ignorar el parámetro -v si no quiere montar el volumen, eso depende de usted. Si no lo hace, es más difícil editar el archivo de configuración .ini si es algo que se quiere hacer.
docker run -it -v <PATH_ON_YOUR_MACHINE_TO_MOUNT>:/opt/data minecraft-console-client:latest
Ahora puede iniciar sesión y el Cliente se estará ejecutando.
Para desacoplarse del cliente pero mantenerlo funcionando en segundo plano presione: CTRL + P y después CTRL + Q.
Para reacoplarse use el comando: docker attach
Iniciar el contenedor usando docker-compose:
Por defecto, el volumen del contenedor se mapea en una nueva carpeta llamada data en la misma carpeta docker-compose.yml está almacenado.
Si no desea mapear un volumen, tiene que ** ** o eliminar la entera sección de volúmenes:
#volúmenes:
#- './data:/opt/data'
Asegúrese de que está en el directorio en el que se almacena docker-compose.yml antes de intentar iniciarlo. Cuando lo haga, puede iniciar el contenedor:
docker-compose run MCC
Recuerde eliminar el contenedor después de usarlo:
docker-compose down
Si utiliza el archivo INI e ingresó sus datos (nombre de usuario, contraseña, servidor) en ese entonces, puede iniciar su contenedor usando:
docker-compose up
docker-compose up -d #para ejecutar deamonized en segundo plano
Tenga en cuenta que no podrá interactuar con el cliente usando docker-compose up. Si desea esa funcionalidad, utilice el primer método: docker-compose run MCC.
Igual que anteriormente, puede detener y remover el contenedor usando:
docker-compose down
Ejecutar en Android
Es posible ejecutar el cliente de la consola de Minecraft en Android a través de Termux y Ubuntu 22.04 en él, sin embargo requiere una configuración manual de varios comandos, tenga cuidado de NO OMITIR ningún paso. Tenga en cuenta que esto puede tardar entre 10 y 20 minutos o más en completar dependiendo de su nivel de conocimiento técnico, Velocidad de Internet y velocidad del CPU.
Tip
Esta sección va a ser un poco técnica, voy a hacer todo lo posible para que sea lo más simple posible. Si tiene problemas para continuar o si encuentra algún problema, no dude en abrir una discusión en nuestro repositorio de Github.
Tip
Necesitas tener algunos conocimientos básicos de Linux, si no sabes nada, mira este video para familiarizarse con los comandos básicos.
Tip
Aquí estaremos instalando todo en la cuenta root por simplicidad, si quieres crear una cuenta de usuario, asegúrate de actualizar el comando que hace referencia al directorio /root con tu directorio de inicio.
Installation
Termux
Warning
La versión de Termux en Play Store está desactualizada y no está soportada, no la utilices, usa la versión oficial en Github.
Vaya a la última versión de Termux en Github, descargue debug_universal.apk, descomprima y ejecute.
Tip
Si tu gestor de archivos no te permite ejecutar archivos APK, instala y usa File Manager + y dale permiso para instalar aplicaciones de terceros cuando se te pregunte.
Danger
Una vez instalado Termux, ábralo, baje el menú de notificaciones, en la notificación de Termux, arrastre hacia abajo hasta que vea las siguientes opciones: Exit | Acquire wakelock, presione en Acquire wakelock y permita a Termux tener permsio de exclusión de optimización de batería cuándo se pregunte. Si no lo haces, ¡tu rendimiento será reducido y Termux podría ser cerrado por Android mientras se ejecuta en segundo plano!
Instalando Ubuntu 22.04
En esta etapa, tienes dos opciones:
- Siguiendo con este mismo tutorial en texto
- Ver un videotutorial en Youtube para instalar Ubuntu en Termux
Tip
If you decide to watch the Youtube tutorial, watch only up to 1:58, the steps after are not needed and might just confuse you.
Para instalar Ubuntu 22.04 en Termux necesitas wget y pRoot, vamos a instalarlos en los siguientes pasos.
Una vez que tenga Termux instalado, ábralo y ejecute el siguiente comando uno tras otro (en orden):
pkg updatepkg upgradepkg install proot wget
Tip
Si se le pide que presione Y/N durante el proceso de actualización(pasos Update/Upgrade), simplemente ingrese Y, y presione Enter
Ahora necesita descargar un script de instalación usando el siguiente comando:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MFDGaming/ubuntu-in-termux/master/ubuntu.sh
Una vez descargado el script, ejecútelo con:
bash ubuntu.sh
Entonces se le hará una pregunta, ingrese Y, y presione Enter.
Una vez finalizada la instalación, puedes iniciar Ubuntu con:
./startubuntu.sh
Tip
Ahora cada vez que abra Termux después de que se haya cerrado, para acceder a Ubuntu tiene que usar este comando
Instalando .NET en ARM
Since there are issues installing .NET 7.0 via the APT package manager at the time of writing, we will have to install it manually.
Primero necesitamos actualizar los repositorios del gestor de paquetes APT e instalar sus dependencias.
Para actualizar los repositorios APT, ejecute el siguiente comando:
apt update -y && apt upgrade -y
Después de hacerlo, necesitamos instalar dependencias para .NET, con el siguiente comando:
apt install wget nano unzip libc6 libgcc1 libgssapi-krb5-2 libstdc++6 zlib1g libicu70 libssl3 -y
After you have installed dependencies, it's time to install .NET, you either can follow this tutorial or the Microsoft one.
Navigate to your /root home directory with the following command:
cd /root
First you need to download .NET 7.0, you can do it with the following command:
wget https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/6cd2eaa7-4c06-4168-b90b-ee2d6bb40b10/4a8387eb07e17d262bfb9965f6d34462/dotnet-sdk-7.0.203-linux-arm64.tar.gz
Tip
This tutorial assumes that you have 64 bit version of ARM processor, if you happen to have a 32-bit version replace the link in the command above with this one
Tip
This tutorial assumes that you're following along and using Ubuntu 22.04, if you're using a different distro, like Alpine, go to here and copy an appropriate link for your distro.
Once the file has been downloaded, you need to run the following commands in order:
DOTNET_FILE=dotnet-sdk-7.0.203-linux-arm64.tar.gzWarning
If you're using a different download link, update the file name in this command to match your version.
export DOTNET_ROOT=/root/.dotnetWarning
Here we're installing .NET in
/root, if you're installing it somewhere else, make sure to set your own path!mkdir -p "$DOTNET_ROOT" && tar zxf "$DOTNET_FILE" -C "$DOTNET_ROOT"export PATH=$PATH:$DOTNET_ROOT:$DOTNET_ROOT/tools
Now we need to tell our shell to know where the dotnet command is, for future sessions, since the commands above just tell this current session where the dotnet is located.
Warning
You will need a basic knowledge of Nano text editor, if you do not know how to use it, watch this Youtube video tutorial
To enable this, we need to edit our /root/.bashrc file with the following command:
nano /root/.bashrc
Scroll down to the bottom of the file using Page Down (PGDN) button, make a new line and paste the following text:
export DOTNET_ROOT=/root/.dotnet/
export PATH=$PATH:$DOTNET_ROOT:$DOTNET_ROOT/tools
Warning
Here we're installing .NET in /root, if you're installing it somewhere else, make sure to set your own path!
Save the file usign the following combination of keys: CTRL + X, type Y and press Enter.
Veryfy that .NET was installed correctly by running:
dotnet
You should get a help page:
root@localhost:~# dotnet
Usage: dotnet [options]
Usage: dotnet [path-to-application]
Options:
-h|--help Display help.
--info Display .NET information.
--list-sdks Display the installed SDKs.
--list-runtimes Display the installed runtimes.
path-to-application:
The path to an application .dll file to execute.
Installing MCC
Finally, we can install MCC.
Warning
If you have a 32 ARM processor, you need to build the MCC yourself, take a look at the Building From Source section. Also make sure to be using the appropriate -r parameter value for your architecture.
Let's make a folder where the MCC will be stored with the following command:
mkdir MinecraftConsoleClient
Then enter it the newly created folder:
cd MinecraftConsoleClient
Download the MCC with the following command:
wget https://github.com/MCCTeam/Minecraft-Console-Client/releases/latest/download/MinecraftClient-linux-arm64.zip
Unzip it with the following command:
unzip MinecraftClient-linux-arm64.zip
You can remove the zip archive now, we do not need it anymore, with:
rm MinecraftClient-linux-arm64.zip
And finally run it with:
./MinecraftClient
After installation
When you run Termux next time, you need to start Ubuntu with: ./startubuntu.sh
Then you can start the MCC again with ./MinecraftClient
To stop MCC from running you can press CTRL + C
To edit the configuration/settings, you need a text editor, we recommend Nano, as it's very simple to use, if you have followed the installation steps above, you should be familiar with it, if not, check out this tutorial.
For downloading files, you can use the wget file we have installed, simply run:
wget your_link_here (you have examples above, and a video tutorial down bellow).
Además, aquí hay algunos tutoriales de linux para personas nuevas:
- Linux Terminal Introduction by ExplainingComputers
- Linux Crash Course - nano (command-line text editor) by Learn Linux TV
- Linux Crash Course - The wget Command by Learn Linux TV
- Linux Basics: How to Untar and Unzip Files (tar, gzip) by webpwnized
Run on a VPS
Tip
This is a new section, if you find a mistake, please report it by opening an Issue in our Github repository. Thank you!
The Minecraft Console Client can be run on a VPS 24 hours, 7 days a week.
- What is a VPS?
- Prerequisites
- Where to get a VPS
- Initial Amazon VPS setup
- Initial VPS setup
- Creating a new user account
- Installing .NET Core 6
- Installing the Minecraft Console Client
What is a VPS?
VPS stands for a Virtual Private Server, it's basically a remote virtual PC that is running in the cloud, 24 hours a day, 7 days in week. To be precise, it's a virtual machine that runs on top of a host operating system (eg. Proxmox).
You can use a VPS for hosting a website, or a an app, or a game server, or your own VPN, or the Minecraft Console Client.
Here is a Youtube video that explains it in more detail if you're interested.
Prerequisites
Gitbash (if you're on Windows)
Download and install Gitbash.
Tip
Make sure to allow the installation to add it to the context menu
sshandssh-keygencommands (On Windows they're available with Gitbash, on macOs and Linux they should be available by default, it not, search on how to install them)Basic knowledge of Linux shell commands, terminal emulator usage, SSH and Nano editor.
If you already know this, feel free to skip.
if you get stuck, watch those tutorials.
If you're new to this, you can learn about it here:
Where to get a VPS
You have 2 options:
Buying a VPS
If you do not want to give your info to Amazon or don't have a debit card, you can buy your own VPS.
What hardware requirements I need for running the MCC?
The MCC is not expensive to run, so it can run on basically any hardware, you do not need to spend a lot of money on a VPS if you are going to run just the MCC, go with the cheapest option.
Where to buy a VPS?
Danger
In this tutorial we will be using Ubuntu 22.04, make sure to select it as the OS when buying a VPS.
Some of the reliable and cheap hosting providers (sorted for price/performance):
Minimum price:
2.50 EUR / monthTip
Does not have Ubuntu 22.04 in the dropdown menu when ordering, you will have to re-install later or ask support to do it.
Minimum price:
3.57 EUR / monthMinimum price:
4.51 EUR / monthMinimum price:
4 EUR / monthMinimum price:
7 EUR / monthMore serious VPS able to host multiple applications, 4 CPU cores and 8 GB of RAM, 200 GB SSD
You also may want to search for better deals.
AWS EC2 VPS
Danger
This will require you to have a valid debit card that can be used on internet and a mobile phone number, as well as giving that info to Amazon corporation.
Warning
Scammers often get AWS VPS and use it to mass login on to stolen Microsoft accounts, some AWS IP addresses might be blocked by Microsoft because of that, if so, you might need to switch regions or to use a Proxy. To debug if your IP has been banned by Microsoft, use the ping <ip> and traceroute <ip> commands.
Warning
Related to the warning above, if you have issues logging with Microsoft and you're not banned, you may want to check the Security center on your account and approve the login from the VPS, this can be the case for some users.
Tip
If you're not banned, sometimes fetching the keys can take some time, try giving it a minute or two, if it still hangs, hit some keys to refresh the screen, or try restarting and running again. If it still happens, use tmux instead of screen.
Register on AWS and enter all of your billing info and a phone number.
Once you're done, you can continue to Setting up the Amazon VPS.
Initial Amazon VPS setup
Tip
Skip this section if you're not using AWS. Go to Initial VPS setup
When you register and open the AWS Console, click on the Search field on the top of the page and search for: EC2
Tip
Make sure to select the region closest to you for the minimal latency
Click on the Launch instance button.
Fill out the Name field with a name of your preference.
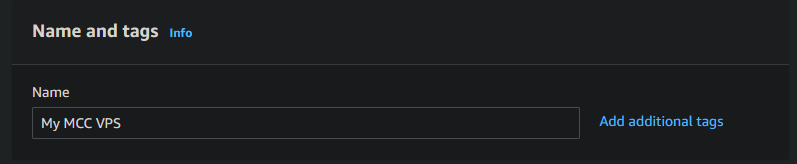
For the Application and OS images select Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS (HVM), SSD Volume Type.
Danger
Make sure that it has Free tier eligible next to it.
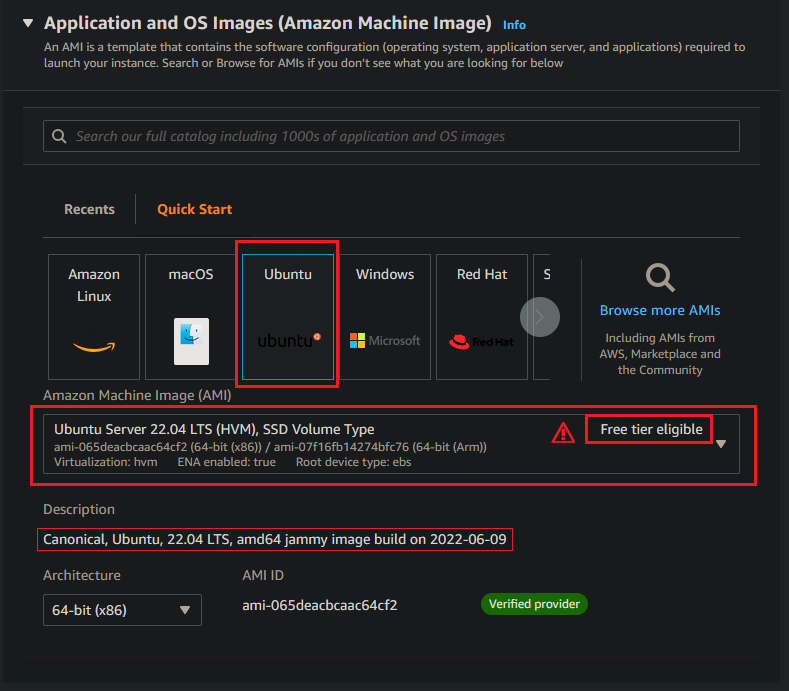
For the Instance type select t2.micro.
For the Key pair (login) click on Create new key pair and name it VpsRoot, leave the rest of settings as default and click Create key pair, this will generate a RSA private key that will be automatically downloaded.
Danger
Make sure that you save this file in a safe place and do not loose it, it's of an upmost importance since it's used to access the root/admin account of the VPS. Without it you will not be able to access the root account of the VPS! Also do not let it fall into wrong hands.
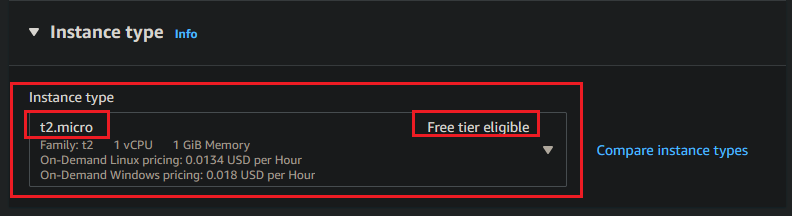
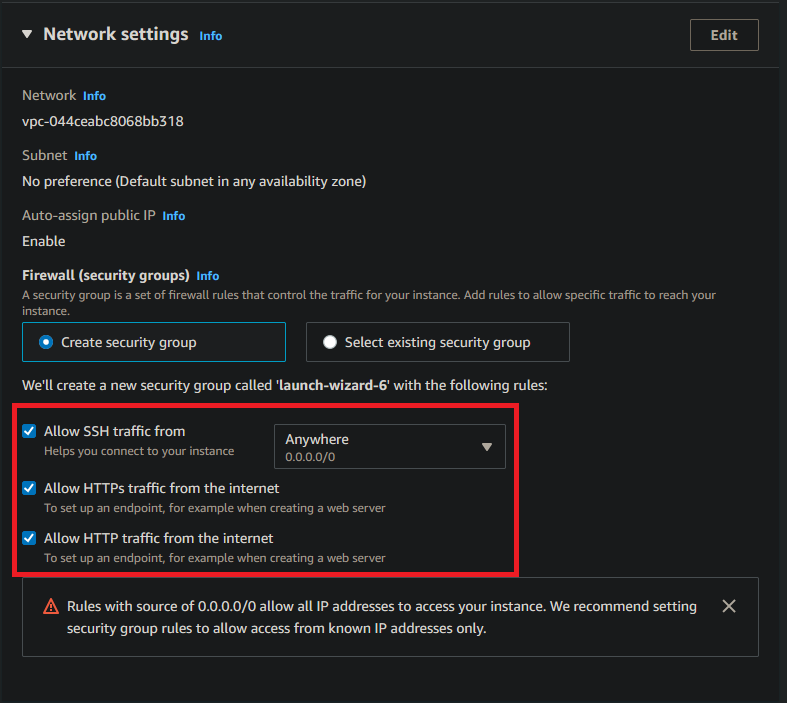
For the Network settings check the following checkboxes on:
Allow SSH traffic from(Anywhere)Allow HTTPs traffic from the internetAllow HTTP traffic from the internet
Tip
The SSH traffic from Anywhere is not the best thing for security, you might want to enter IP addresses of your devices from which you want to access the VPS manually.
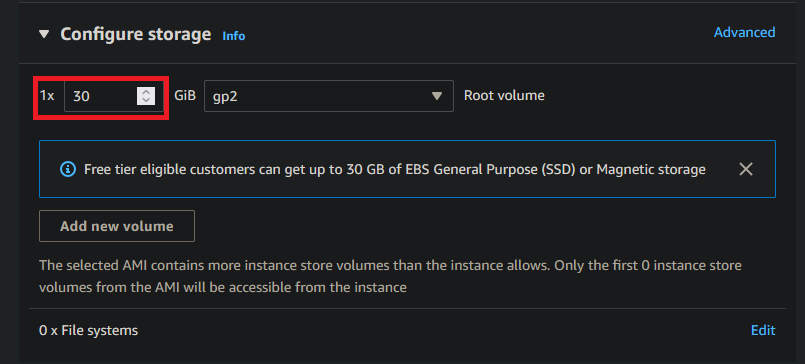
For the Storage enter 30.
Finally, review the Summary confirm that everything is as in the tutorial and that you will not be charged and click on the Launch instance. Once you've clicked on the button, it will take a couple of minutes for the instance to be available up and running.
Once the instance is up and running, go to it's details and copy the Public DNS v4 IP.
You now need to login, go to your folder where you keep the private key you've generated and downloaded (make sure you make a new folder for it, do not keep in the downloads folder) and right click on the empty white space (not on files), if you're on Windows click Git Bash here, on mac OS and Linux click on Open Terminal (or whatever it is called).
In order to login with SSH, you are going to use the following command:
ssh -i <name of your private root key here> ubuntu@<your public dns v4 ip here>
Tip
< and > are not typed, that is just a notation for a placeholder!
Tip
ubuntu is a default root account username for Ubuntu on AWS!
Example:
ssh -i VpsRoot.pem ubuntu@ec2-3-71-108-69.eu-central-1.compute.amazonaws.com
If you've provided the right info you should get Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS message.
Now you can continue to Creating a new user
Initial VPS setup
Tip
This section if for those who do not use AWS, if you use AWS skip it
When you order the VPS, most likely you will be asked to provide the root account name and password, if it is the case, name the account as root and give it a password of your choice.
Other option is that you will get your login info in the email once the setup is done.
Once you have the root login account info, you need Gitbash on Windows and ssh if you're on macOS or Linux (if you do not have it by some chance, search on how to install it, it is simple).
If you're on Windows open Git Bash, on mac OS and Linux open a Terminal and type the following command:
ssh <username>@<ip>
Tip
If you're given a custom port other than 22 by your host, you should add -p <port here> before the username (eg. ssh -p <port here> <username>@<ip>) or :<port> after the ip (eg. ssh <username>@<ip>:<port>)
Example:
ssh root@142.26.73.14
Example with port:
ssh -p 2233 root@142.26.73.14
Once you've logged in you should see a Linux prompt and a welcome message if there is one set by your provider.
Creating a new user
Once you've logged in to your VPS you need to create a new user and give it SSH access.
In this tutorial we will be using mcc as a name for the user account that will be running the MCC.
Tip
You may be wondering why we're creating a separate user account and making it be accessible over SSH only. This is for security reasons, if you do not want to do this, you're free to skip it, but be careful.
To create a new user named mcc execute the following command:
sudo useradd mcc -m
Now we need to give it a password, execute the following command, type the password and confirm it:
sudo passwd mcc
Tip
When you're typing a password it will not be displayed on the screen, but you're typing it for real.
Tip
Make sure you have a strong password!
Now we need to give our user account the admin permissions:
sudo usermod -aG sudo mcc
Now we are going to set it's shell to bash:
sudo chsh mcc -s /bin/bash
Now we need to log in as the mcc user:
su mcc
Fill in your password when asked.
Navigate to the mcc user home directory with:
cd ~
Make a new .ssh directory:
mkdir .ssh
Enter it with:
cd .ssh
Make a new empty file named authorized_keys:
touch authorized_keys
Do no close the Git bash/Terminal emulator.
On your PC, make a new folder where you are going to store your SSH keys that you're going to use to log in to the user account.
Open the folder, and right click on the empty white space (not on files), if you're on Windows click Git Bash here, on mac OS and Linux click on Open Terminal (or whatever it is called).
Type the following command:
ssh-keygen -t RSA -b 4096
Enter the name of the key file to be: MCC_Key, press Enter.
When asked for a passphrase, enter a password of your choice and confirm it, make sure it's strong and that you remember it, best if you write it down on a piece of paper.
This will generate a private and a public key that you will use to log in to the VPS as a user that you've created.
Now open the MCC_Key.pub file with a text editor of your choice and copy it's contents to the clipboard.
Return to the Git Bash/Terminal emulator and execute the following command:
sudo apt install nano -y
This will install the Nano editor on your VPS.
Now we need to let the SSH service on your VPS know about your newly generated SSH key pair.
Make sure you are in the /home/mcc/.ssh folder, you can confirm this by executing:
pwd
If it does not print /home/mcc/.ssh, navigate to it with:
cd /home/mcc/.ssh
Now you need to open the authorized_keys file with the nano editor:
nano authorized_keys
Now paste the copied contents of the MCC_Key.pub into the nano editor by right clicking on it.
Save the file with CTRL + O, press Enter, and then exit it with CTRL + X.
Now we need to configure the SSHD service to let us login with the SSH key we have generated, for this we need to edit the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file with nano:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Find the #PubkeyAuthentication yes line and remove the # in front to uncomment the line.
Then find the #AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys .ssh/authorized_keys2 line and remove the # to uncomment the line.
Additionally for better security you can do the following:
- Set
PermitRootLogintoyes - Change the
Portto some number of your choice (22-65000) (Make sure it's at least 2 digits and avoid common ports used by other apps like: 21, 80, 35, 8080, 3000, etc...) - Uncomment
#PasswordAuthentication yesby removing the#in front and set it toyes(This will disable password login, you will be able to login with SSH keys only!)
Save the file with CTRL + O, hit Enter, close it with CTRL + X.
Now we need to restart the SSHD service with:
sudo systemctl restart sshd
Let's check if everything is working correctly:
sudo systemctl status sshd
If everything has been configured as it should be you should see active (running) as a status of the service.
If not, open the config file again and check for mistakes.
Press q to exit the log mode.
Logout from the mcc user with exit command, and then logout from the root ubuntu user by typing exit again.
Now we can login to the user with our private MCC_Key file.
Command:
ssh -i <path to the MCC_Key private key> mcc@<ip here>
Example:
ssh -i MCC_Key mcc@3.71.108.69
Tip
If you've changed the Port, make sure you add a -p <your port here> option after the -i <key> option (eg. ssh -i MCC_Key -p 8973 mcc@3.71.108.69)!
If did everything correctly you should see a Linux prompt and a welcome message if there is one on your provider.
You can do whoami to see your username.
Now you can install .NET Core 7 and MCC.
Installing .NET Core 7
Tip
If your VPS has an ARM CPU, follow this part of the documentation and then return to section after this one.
Warning
With newer versions of .NET Core 7 on Ubuntu 22.04 you might get the following error: A fatal error occurred, the folder [/usr/share/dotnet/host/fxr] does not contain any version-numbered child folders, if you get it, use this solution
Log in as the user you've created.
Update the system packages and package manager repositories:
sudo apt update -y && sudo apt upgrade -y
Install wget:
sudo apt install wget -y
Go to your home directory with:
cd ~
Download the Microsoft repository file:
wget https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/22.04/packages-microsoft-prod.deb -O packages-microsoft-prod.deb
Add Microsoft repositories to the package manager:
sudo dpkg -i packages-microsoft-prod.deb
Remove the file, we do not need it anymore:
rm packages-microsoft-prod.deb
Finally, install .NET Core 7:
sudo apt-get update -y && sudo apt-get install -y dotnet-sdk-7.0
Run the following command to check if everything was installed correctly:
dotnet
You should get:
Usage: dotnet [options]
Usage: dotnet [path-to-application]
Options:
-h|--help Display help.
--info Display .NET information.
--list-sdks Display the installed SDKs.
--list-runtimes Display the installed runtimes.
path-to-application:
The path to an application .dll file to execute.
If you do not get this output and the installation was not successful, try other methods.
If it was successful, you can now install the MCC.
Installing MCC on a VPS
Now that you have .NET Core 7.0 and a user account, you should install the screen utility, you will need this in order to keep the MCC running once you close down the SSH session (if you do not have it, the MCC will just stop working once you disconnect). You can look at the screen like a window, except it's in a terminal, it lets you have multiple "windows" open at the same time.
Tip
There is also a Docker method, if you're using Docker, you do not need the screen program.
You also can learn about the screen command from this Youtube tutorial.
To install the screen execute the following command:
sudo apt install screen -y
Now you can install the MCC:
- Descarga los binarios compilados
- Compilar desde el código fuente
- Run using Docker (Doesn't require the
screencommand)
How to use the screen command?
Warning
If you have issues with Screen command, like output not being properly formatted or program handing/freezing, try using tmux, click here to learn how to use it.
To start a screen, type:
screen -S mcc
Tip
mcc here is the name of the screen, you can use whatever you like, but if you've used a different name, make sure you use that one instead of the mcc in the following commands.
Tip
You need to make a screen only once, however if you reboot your VPS, you need to start it on each reboot.
Now you will be in the screen, now you can start the MCC and detach from the screen.
To detach from the screen press CTRL + A + D.
To re-attach/return to the screen, execute the following command:
screen -r mcc
If you've accidentally closed the SSH session without detaching from the screen it might be still attached, to detach it use:
screen -d mcc
To list out screens you can use:
screen -ls
To stop the MCC, you can hit CTRL + D (hit it few times).